Cylindrical roller bearings are a crucial component in various industries, offering unique advantages and facing certain limitations. Understanding their structure, advantages, and disadvantages is essential for making informed decisions in engineering and machinery applications.
What Is a Cylindrical Roller Bearing?
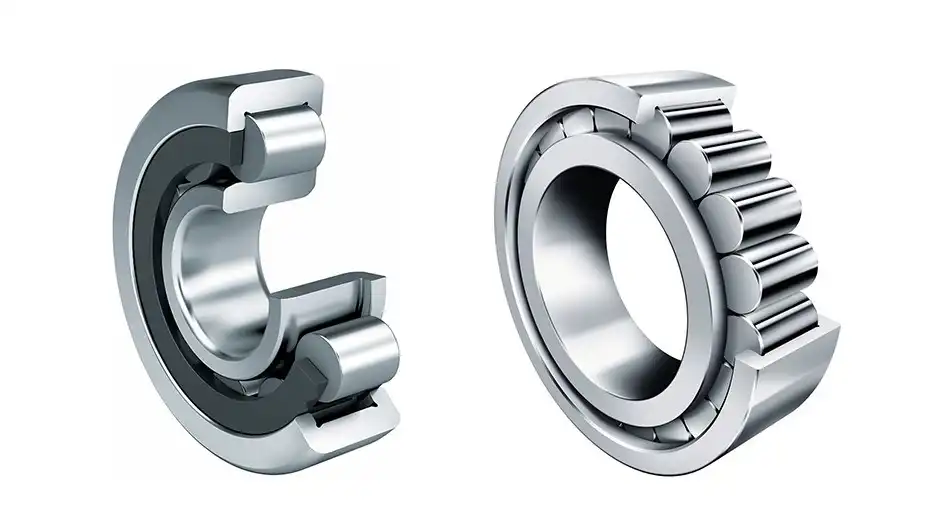

A cylindrical roller bearing is a vital mechanical component designed to facilitate smooth and efficient rotation in various machinery and industrial applications. It falls under the category of rolling element bearings, which are crucial for reducing friction between moving parts.
Structure of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
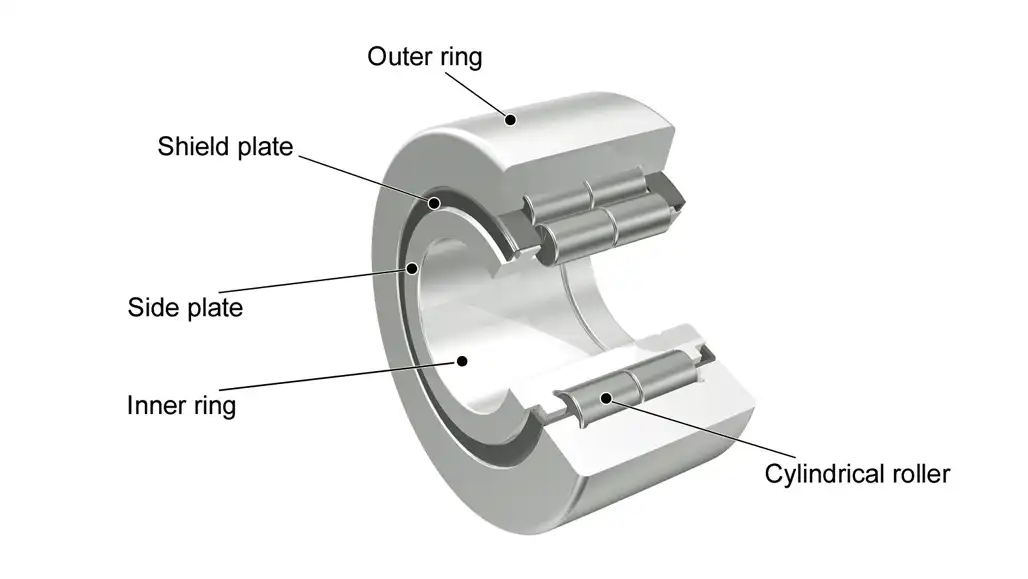
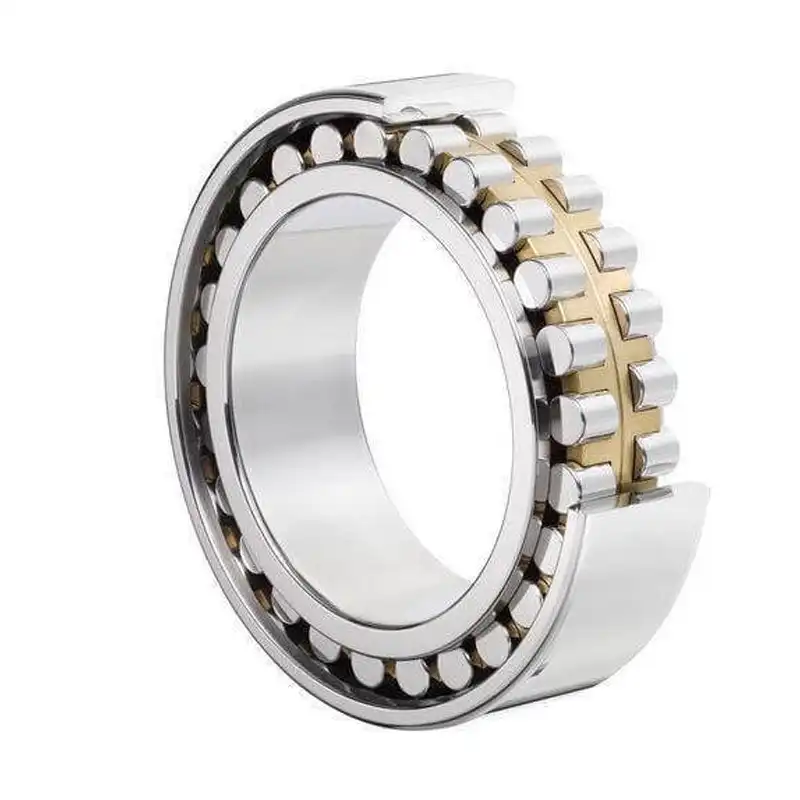
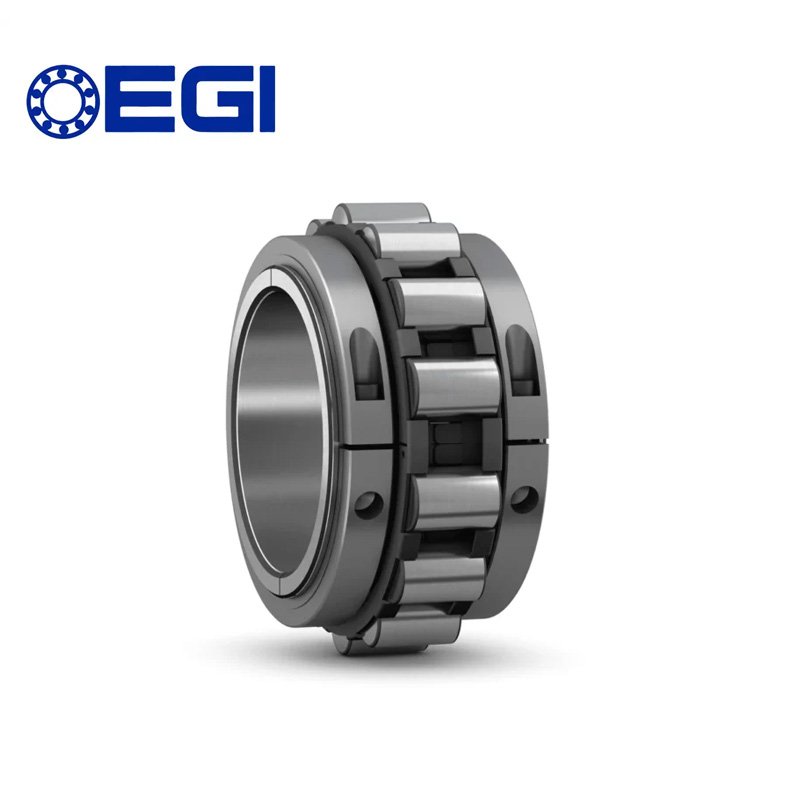
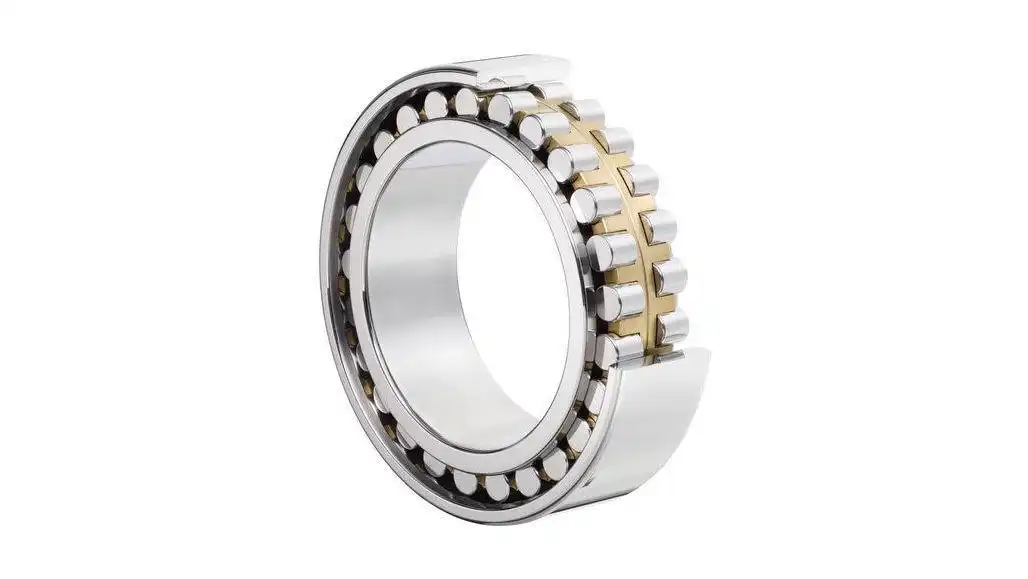
Cylindrical roller bearings are intricately designed components essential for enabling smooth rotation in machinery and various mechanical applications. Understanding their structure is key to appreciating their functionality. Here’s a breakdown of the components that constitute a typical cylindrical roller bearing:
Inner and Outer Rings:
The bearing comprises two rings – an inner ring and an outer ring. These rings form the main body of the bearing, providing a stable structure for the other components.
Roller Elements:
Cylindrical roller bearings get their name from the cylindrical-shaped rollers positioned between the inner and outer rings. These rollers are crucial for distributing loads evenly and facilitating rotation.
Cage or Separator:
Positioned between the rollers, the cage or separator serves the vital function of maintaining proper spacing between the cylindrical rollers. This ensures that the rollers move smoothly along the raceways of the inner and outer rings without interference.
Raceways:
The inner and outer rings have specially designed surfaces known as raceways. These raceways guide the movement of the cylindrical rollers, allowing them to transmit radial loads effectively.
Retainer:
Some cylindrical roller bearings incorporate a retainer, which is a component that holds the rollers in place within the cage. It prevents the rollers from touching each other, reducing friction and wear.
Understanding the synergy of these components is crucial for engineers and technicians involved in selecting and maintaining cylindrical roller bearings. The careful arrangement of inner and outer rings, roller elements, and separators ensures that these bearings can handle radial loads efficiently while maintaining durability and reliability in various industrial applications.
Advantages of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
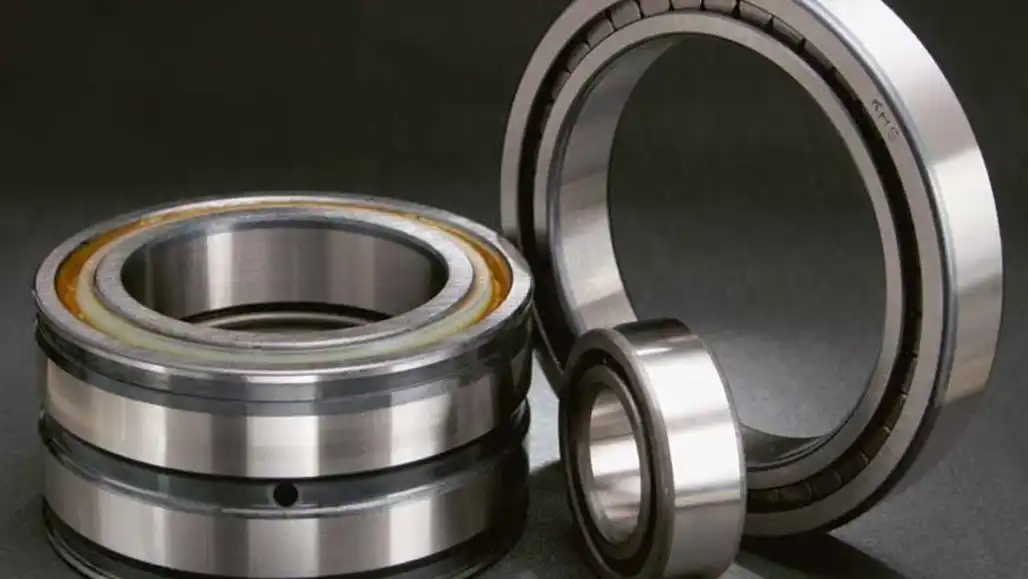

Cylindrical roller bearings offer a multitude of advantages, making them indispensable components in various industrial applications. Understanding these advantages is crucial for engineers and designers seeking optimal solutions for their machinery. Here are the key benefits associated with cylindrical roller bearings:
High Radial Load Capacity:
Cylindrical roller bearings excel in handling radial loads. Their design, with cylindrical rollers positioned perpendicular to the axis, allows for efficient distribution of radial forces. This makes them ideal for applications where radial loads are predominant.
Better Shock Absorption:
The cylindrical shape of the rollers and their alignment in the bearing structure contribute to effective shock absorption. This is particularly advantageous in machinery and equipment where sudden impacts or vibrations are common, providing smoother and more reliable operation.
Low Friction:
Cylindrical roller bearings exhibit low friction characteristics, reducing energy consumption and minimizing heat generation during operation. The result is improved overall efficiency and reduced wear and tear on the bearing components.
Versatility in Applications:
These bearings find extensive use in various industrial settings, including the automotive industry and machinery applications. Their versatility stems from the ability to handle different types of loads, making them suitable for a wide range of equipment.
Space-Efficient Design:
The compact design of cylindrical roller bearings allows for space efficiency in machinery. This is particularly advantageous in applications where minimizing size and weight is crucial without compromising load-bearing capabilities.
Ease of Installation:
Cylindrical roller bearings are relatively easy to install, making them convenient for maintenance and replacement tasks. This ease of installation contributes to reduced downtime in industrial operations.
Long Service Life:
Properly maintained cylindrical roller bearings have a long service life. The efficient load distribution and low friction characteristics contribute to durability, resulting in extended periods of reliable performance.
Suitability for High-Speed Operation:
In certain configurations, cylindrical roller bearings are well-suited for high-speed applications. This makes them valuable in industries where rotational speed is a critical factor.
Understanding these advantages empowers engineers and industry professionals to make informed decisions when selecting bearings for specific applications. The combination of high radial load capacity, shock absorption, low friction, and versatility positions cylindrical roller bearings as essential components in the machinery landscape.
Cylindrical Roller Bearings Benefits

Here are some benefits of cylindrical roller bearings in the following:
Greater Radial Load Capacity:
Cylindrical roller bearings excel in handling radial loads, providing superior capacity compared to ball bearings. This makes them ideal for cylindrical roller bearing applications with heavy radial forces.
High-Speed Capability:
The roller design of cylindrical roller bearings allows them to accommodate faster speeds compared to other types of roller bearings. This capability is crucial in applications requiring efficient rotation at elevated speeds.
Resistance to Fatigue Damage:
Cylindrical roller bearings are designed to resist damage from fatigue, ensuring durability and prolonged service life even under continuous or fluctuating loads.
Straight or Tapered Diameters:
These bearings offer versatility with options for straight or tapered outside and inside diameters. This adaptability caters to diverse applications, allowing for precise fits and optimal load distribution.
Flush Inside the Housing:
The design of cylindrical roller bearings ensures a flush fit inside the housing, enhancing stability and reducing the risk of misalignment. This feature contributes to smoother and more reliable operation.
Ease of Installation:
Cylindrical roller bearings are easy to install, simplifying the assembly process. This not only reduces the risk of installation damage but also contributes to quicker and more efficient setup.
Space and Weight Savings:
With a slim and compact design, cylindrical roller bearings save both space and weight in machinery. This makes them advantageous in applications where minimizing size and weight is crucial.
Variety in Sizes and Materials:
Cylindrical roller bearings come in several sizes and materials, providing flexibility for different applications. The availability of various options allows engineers to choose bearings that best suit specific operational requirements.
Understanding these benefits allows engineers and industry professionals to leverage the advantages of cylindrical roller bearings in designing and maintaining efficient machinery across a wide range of applications.
Disadvantages of Cylindrical Roller Bearings

While cylindrical roller bearings offer numerous advantages, it’s important to consider their limitations and disadvantages. Engineers and designers should be aware of these aspects to make informed decisions about their suitability for specific applications. Here are the key disadvantages associated with cylindrical roller bearings:
Limited Axial Load Capacity:
One notable limitation is the relatively lower axial load capacity compared to other types of bearings. Cylindrical roller bearings are primarily designed for radial loads, and their performance may be suboptimal in applications with significant axial forces.
Sensitivity to Misalignment:
Cylindrical roller bearings can be sensitive to misalignment between the inner and outer rings. Misalignment can lead to uneven distribution of loads, increased friction, and premature wear, impacting the bearing’s overall performance.
Higher Cost:
In some cases, cylindrical roller bearings may have a higher initial cost compared to alternative bearing types. This cost consideration could be a factor in budget-conscious projects or applications.
Complex Design:
The design of cylindrical roller bearings can be more complex compared to simpler bearing types. This complexity may result in challenges during maintenance, repair, or replacement, especially for those without specialized knowledge.
Increased Friction at High Speeds:
While generally suitable for high-speed applications, certain configurations of cylindrical roller bearings may experience increased friction at very high speeds. Engineers need to carefully consider the specific requirements of their applications.
Space Requirements:
Although generally space-efficient, the design of cylindrical roller bearings may not be the most compact in all scenarios. Applications with stringent space constraints might benefit from alternative bearing types.
Potential for Heat Generation:
Under heavy loads or inadequate lubrication, cylindrical roller bearings may generate more heat than desired. Excessive heat can lead to premature wear and reduce the overall lifespan of the bearing.
Maintenance Requirements:
Proper maintenance is crucial for the performance and longevity of cylindrical roller bearings. Regular inspections, lubrication, and alignment checks are necessary, and neglecting maintenance can lead to issues.
Understanding these disadvantages allows engineers to weigh the pros and cons when choosing bearings for specific applications. While cylindrical roller bearings offer exceptional performance in many scenarios, addressing these limitations is essential to ensure optimal functionality and longevity.
Applications in Industrial Settings:
The automotive industry widely uses cylindrical roller bearings due to their ability to handle radial loads. They are also prevalent in various machinery and equipment where reliability and load-bearing capacity are critical.
Limitations and Disadvantages:
While these bearings excel in radial loads, their axial load capacity is limited. Sensitivity to misalignment and a relatively higher cost compared to alternative bearings are notable disadvantages.
Tips for Extending Bearing Lifespan

Ensuring the longevity of cylindrical roller bearings is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and reliability of machinery. Here are essential tips to extend the lifespan of these bearings:
Proper Lubrication:
Adequate lubrication is paramount for reducing friction and preventing wear. Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubricant type, quantity, and intervals. Regularly check and replenish lubrication to maintain optimal conditions.
Correct Mounting Procedures:
Precise mounting is critical to prevent misalignment and uneven load distribution. Follow the recommended mounting procedures outlined by the bearing manufacturer. Use proper tools and techniques to avoid unnecessary stress on the bearing components.
Regular Inspections:
Implement a routine inspection schedule to identify potential issues early. Check for signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment. Promptly address any abnormalities to prevent further damage.
Appropriate Sealing:
Ensure that the bearings are adequately sealed to protect them from contaminants such as dust and moisture. Proper seals prevent premature wear and extend the bearing’s overall lifespan.
Avoid Overloading:
Adhere to the specified load capacities and operating conditions outlined by the manufacturer. Overloading can lead to increased friction, heat generation, and premature failure. Consider the application’s demands and select bearings accordingly.
Temperature Control:
Monitor and control operating temperatures. Excessive heat can degrade lubricants and accelerate wear. Implement cooling mechanisms if necessary and operate within the recommended temperature range.
Alignment Checks:
Regularly check and adjust the alignment of the machinery to prevent misalignment issues. Misalignment places additional stress on bearings, leading to uneven wear and potential damage.
Balanced Loads:
Ensure that loads are distributed evenly across multiple bearings in the system. Balanced loads prevent overloading on individual bearings and contribute to a more uniform wear pattern.
Proper Handling and Storage:
Exercise caution during handling and storage to prevent damage to bearing surfaces. Store bearings in a clean and dry environment, and avoid exposing them to excessive shocks or vibrations.
Utilize Condition Monitoring:
Implement condition monitoring technologies to track the health of bearings in real-time. Vibration analysis, temperature monitoring, and other predictive maintenance techniques can identify issues before they escalate.
Educate Maintenance Personnel:
Ensure that maintenance personnel are well-trained and knowledgeable about the specific requirements of cylindrical roller bearings. Proper handling, installation, and maintenance practices are essential for maximizing lifespan.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:
Always adhere to the guidelines provided by the bearing manufacturer. These guidelines contain critical information on maintenance, operating conditions, and troubleshooting specific to the bearing type.
By incorporating these tips into maintenance practices, engineers and technicians can significantly extend the lifespan of cylindrical roller bearings, promoting reliable and efficient operation in various industrial applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cylindrical roller bearings offer unique advantages in handling radial loads efficiently. However, users must carefully consider their limitations and weigh them against specific application requirements. Technological advancements continue to shape the future of these bearings, ensuring ongoing improvements.





