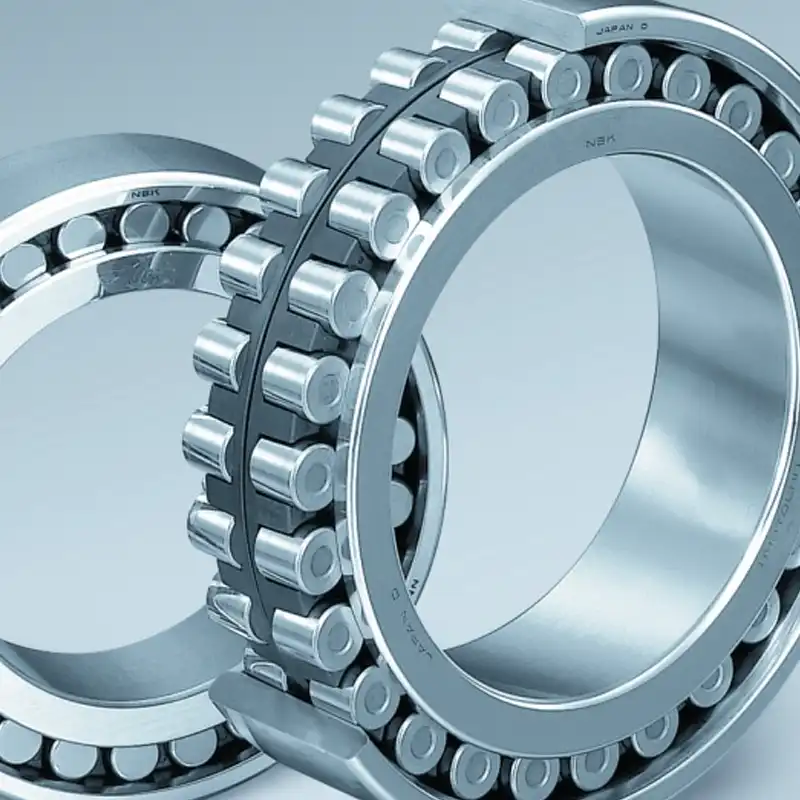
Here are various types of bearings in the industry, and cylindrical roller bearings play a pivotal role in ensuring smooth operation and reducing friction in rotating machinery. These bearings are designed to handle radial loads and are widely used across different industries.
Whether you are involved in manufacturing or maintenance, having a comprehensive understanding of the various types of cylindrical roller bearings is crucial for optimal performance.
What Are Cylindrical Roller Bearings
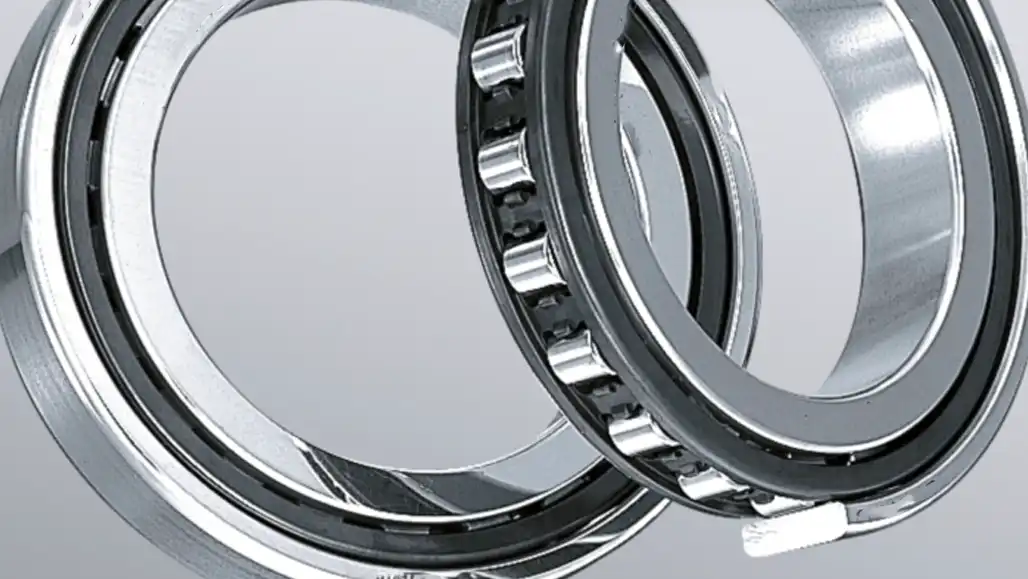

At its core, a cylindrical roller bearing consists of an inner ring, an outer ring, cylindrical rollers, and a cage. The design principles aim to distribute loads evenly, ensuring efficient operation under different conditions. The cylindrical shape of the rollers enables them to accommodate radial loads, making these bearings suitable for a wide range of applications.
Advantages of Cylindrical Roller Bearings

High Load-Carrying Capacity
One of the primary advantages of cylindrical roller bearings is their exceptional load-carrying capacity. The design allows for the distribution of radial loads, making them ideal for applications where heavy loads are prevalent.
Precision and Durability
Cylindrical roller bearings are known for their precision and durability. The arrangement of rollers and the overall design contribute to high-performance levels and a longer lifespan compared to other bearing types.
Application Versatility
The versatility of cylindrical roller bearings is evident in their ability to adapt to various applications. From automotive components to industrial machinery, these bearings find application in a myriad of industries.
Types of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
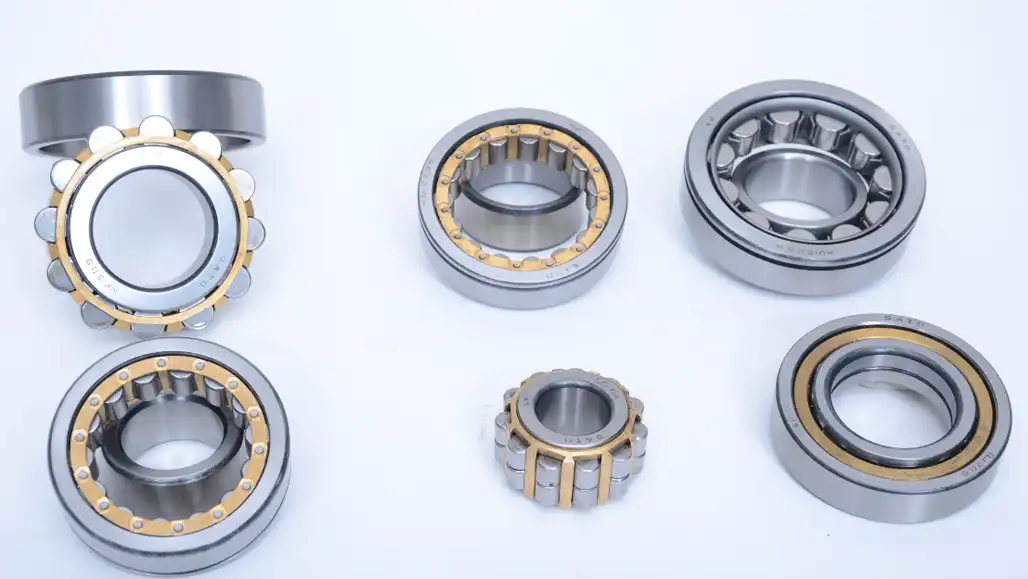

There are several types of cylindrical roller bearings, each catering to specific needs and applications. Let’s explore some common types:
Single Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Single row cylindrical roller bearings consist of one set of cylindrical rollers and are suitable for moderate radial loads. They are widely used in applications where space is a constraint.
Double Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Double row cylindrical roller bearings have two sets of cylindrical rollers, providing increased radial load capacity. This type is often preferred in applications requiring higher load-carrying capabilities.
Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Full complement cylindrical roller bearings feature maximum possible number of rollers, eliminating the need for a cage. This design enhances load-carrying capacity and is suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Multi-Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Multi-row cylindrical roller bearings are designed for extremely heavy radial loads and often find application in industries like steel manufacturing and mining.
Axial Cylindrical Roller Bearing
An axial cylindrical roller bearing is a type of roller bearing designed to carry high axial loads, providing robust rigidity and supporting axial forces in a single direction. It surpasses axial needle roller bearings of the same diameter in terms of load-carrying capacity. These bearings are well-suited for applications where high axial and shock loads occur in one direction, and there are no radial loads present.
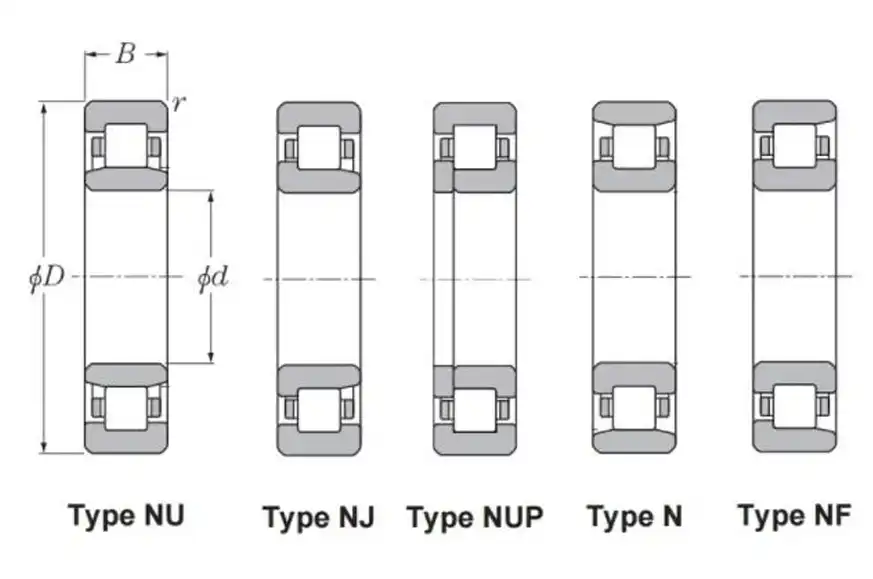
N Type Cylindrical Roller Bearing:
- Designation: The “N” in N Type stands for the outer ring has one integral flange, while the inner ring is without flange.
- Application: N Type bearings are suitable for applications where axial displacement between the shaft and housing is acceptable in one direction.
- Characteristics:
- Designed to accommodate heavy radial loads.
- Can handle moderate axial loads in one direction.
- Generally used in applications where axial movement is possible and one side is fixed.
- Commonly used in gearboxes, electric motors, and industrial machinery.
NU Type Cylindrical Roller Bearing:
- Designation: The “NU” signifies that the outer ring has no integral flanges, while the inner ring has two integral flanges.
- Application: NU Type bearings are suitable for applications where axial displacement between the shaft and housing is needed in both directions.
- Characteristics:
- Ideal for applications with high radial loads.
- Can accommodate axial loads in both directions.
- Suitable for use as non-locating bearings in axial displacement scenarios.
- Widely used in construction equipment, pumps, and machine tool spindles.
NUP Type Cylindrical Roller Bearing:
- Designation: The “NUP” indicates that one integral flange on the outer ring and two loose flanges on the inner ring.
- Application: NUP Type bearings are suitable for applications where axial displacement is limited in both directions or if a locating bearing is needed.
- Characteristics:
- Designed to handle both radial and axial loads.
- Capable of accommodating limited axial displacement in both directions.
- Commonly used in applications where shafts are axially fixed in both directions.
- Found in gearboxes, pumps, and heavy machinery.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines when selecting and installing cylindrical roller bearings to ensure proper functioning and longevity.
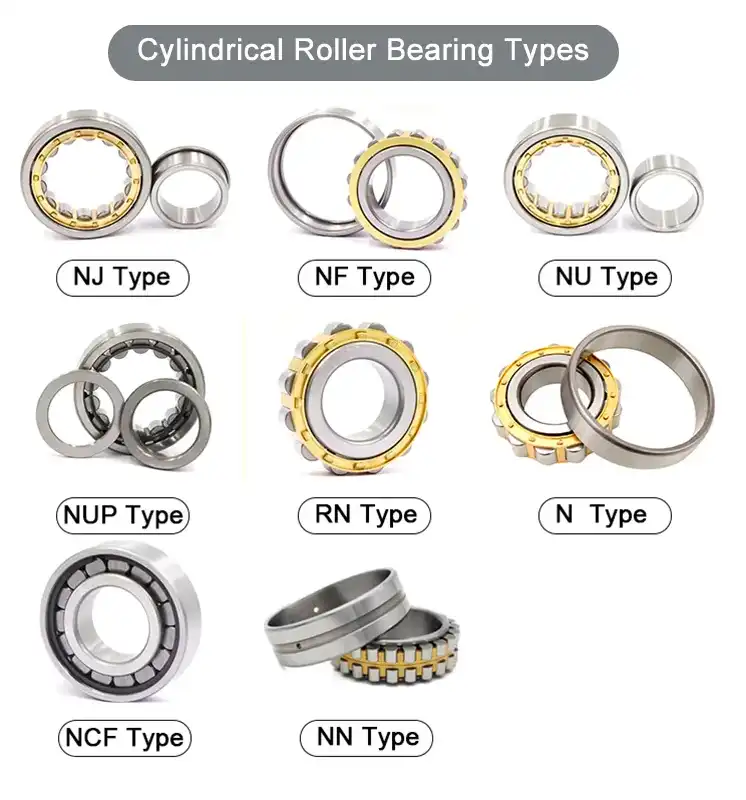

Here’s a table summarizing various types of cylindrical roller bearings:
| Bearing Type | Designation | Outer Ring Flanges | Inner Ring Flanges | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NJ Type | NJ | Two integral | Two integral | Suitable for axial displacement in one direction |
| NF Type | NF | One integral | Two integral | Designed for applications with axial loads |
| NU Type | NU | None | Two integral | Accommodates axial displacement in both directions |
| NUP Type | NUP | One integral | Two loose | Used when axial displacement is limited in both directions |
| RN Type | RN | None | None | Used in applications with radial loads only |
| N Type | N | One integral | None | Accommodates heavy radial loads with limited axial load capacity |
| NCF Type | NCF | Two integral | Two integral | Suitable for applications requiring full complement of rollers |
| NN Type | NN | None | Two integral | Designed to handle heavy radial and axial loads |
Factors Influencing Bearing Selection

When selecting cylindrical roller bearings, several factors come into play to ensure optimal performance:
Load Requirements
Understanding the magnitude and type of loads the bearing will be subjected to is crucial. Whether it’s radial or axial loads, selecting the appropriate type ensures the longevity of the bearing and the machinery it supports.
Speed Considerations
Different bearing types have varying speed capabilities. Considering the operational speed of the machinery is essential to prevent issues such as overheating and premature wear.
Temperature and Environment
The operating environment, including temperature and potential contaminants, influences the choice of bearing material and design. Bearings used in harsh conditions may require special coatings or seals to maintain performance.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Proper installation and maintenance are paramount for the longevity and efficiency of cylindrical roller bearings:
Proper Handling and Storage
- Handle bearings with care, avoiding drops or impacts.
- Store bearings in a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination.
Lubrication Guidelines
- Follow manufacturer recommendations for lubrication.
- Ensure proper lubrication intervals to prevent premature wear.
Periodic Maintenance Recommendations
- Regularly inspect bearings for signs of wear or damage.
- Replace bearings as recommended by the manufacturer or when wear is evident.
Comparing Cylindrical Roller Bearings with Other Types
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of cylindrical roller bearings in comparison to other bearing types is crucial for informed decision-making:
Spherical Roller Bearings
While spherical roller bearings offer excellent alignment capabilities, cylindrical roller bearings are often preferred for applications with higher radial loads.
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are suitable for applications with both radial and axial loads but may have lower radial load capacity compared to cylindrical roller bearings.
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings are compact and lightweight, making them suitable for applications with limited space. However, they may not handle heavy radial loads as effectively as cylindrical roller bearings.
Cylindrical Roller Bearing Applications
Cylindrical roller bearings find applications in various industries, showcasing their adaptability and reliability:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, cylindrical roller bearings are commonly used in wheel hubs, transmissions, and engines due to their load-carrying capacity and durability.
Heavy Machinery
Industries dealing with heavy machinery, such as construction and mining, rely on cylindrical roller bearings for their ability to handle substantial radial loads.
Aerospace Applications
The aerospace industry utilizes cylindrical roller bearings in aircraft engines and landing gear systems, where precision and reliability are critical.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the various types of cylindrical roller bearings is essential for anyone dealing with machinery and rotating components.
From single-row to multi-row configurations, each type serves a specific purpose in handling loads and ensuring smooth operation. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance contribute to the longevity and efficiency of these bearings, making them indispensable in various industries.

