Angular contact balling bearings and deep groove ball bearings are two representative roller bearings, within the bearing types.
Angular contact balling bearings and deep groove ball bearings are widely used to bear radial load and axial load for various machinery.
They are appropriate for high-speed rotation and situations that demand minimal noise and vibration. They come with a steel dust cover.
Alternatively, sealed bearings with rubber seals are pre-filled with grease. Bearings with a stop ring or flange on the outer ring are easily positioned in the axial direction and installed in the housing.
The maximum load-bearing capacity is identical to that of the standard bearing, but there is an additional filling groove in both the inner and outer rings, which enhances the number of balls and increases the rated load.
Let’s embark on a journey to understand these engineering marvels, their distinctions, and their applications.
What Is Angular Contact Ball Bearing
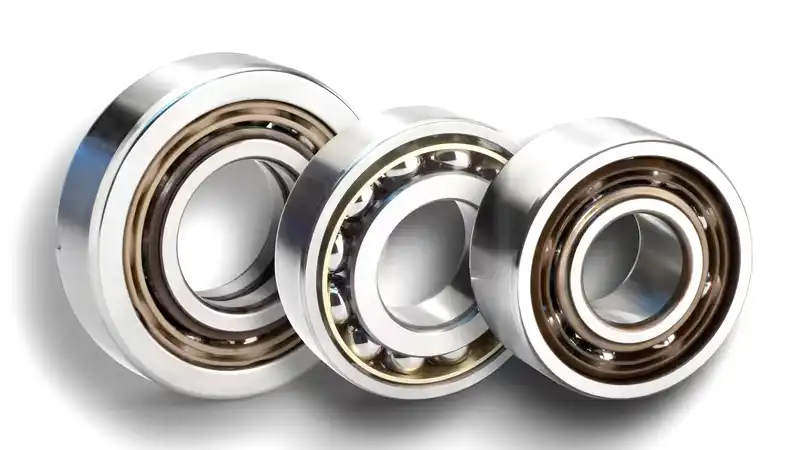

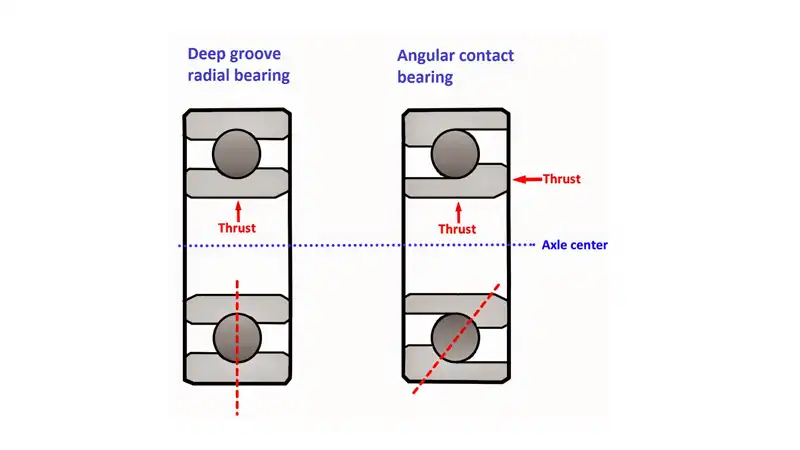
An angular contact ball bearing is a type of precision rolling-element bearing designed to support axial loads in a specific direction. Unlike deep groove ball bearings that primarily handle radial loads, angular contact ball bearings are engineered to accommodate both radial and axial forces, making them suitable for applications where thrust or axial load support is crucial.
Key features of angular contact ball bearings include:
- Contact Angle: Angular contact ball bearings have a contact angle between the raceway and the balls. This angle is critical in determining the bearing’s ability to withstand axial loads. Typically, angular contact bearings have contact angles larger than 15 degrees.
- Load Distribution: These bearings are designed to distribute the load unevenly between the radial and axial directions. This configuration allows them to handle higher axial loads compared to deep groove ball bearings.
- High-Speed Operation: Angular contact ball bearings are well-suited for applications requiring high operational speeds. The design minimizes friction and heat generation, enabling efficient performance at elevated speeds.
- Precision and Rigidity: Angular contact bearings are known for their precision and rigidity. They are commonly used in applications where maintaining accurate shaft positioning and high rigidity are essential, such as in machine tool spindles.
- Matched Sets: In some applications, angular contact ball bearings are used in matched sets. This involves using pairs of bearings with precisely controlled tolerances to enhance load distribution and improve overall performance.
Typical applications for angular contact ball bearings include woodworking spindles, machine tool spindles, vacuum pumps, the semiconductor industry, and centrifuges. Their versatility in handling both radial and axial loads, coupled with high-speed capabilities, makes them crucial components in various precision machinery and rotating equipment.
What Is Deep Groove Ball Bearing
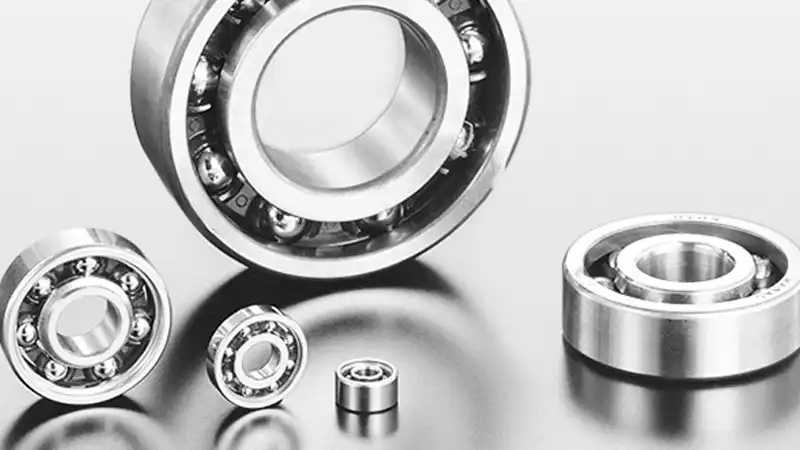

A deep groove ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing known for its versatility in handling radial loads. It is one of the most commonly used bearings due to its simple design, cost-effectiveness, and widespread applicability across various industries.
Key features of deep groove ball bearings include:
- Radial Load Capacity: Deep groove ball bearings are primarily designed to support radial loads, which are forces acting perpendicular to the shaft. They are well-suited for applications where the main load is in the radial direction.
- Deep Groove Design: The name “deep groove” comes from the geometry of the bearing, which has a deep raceway that enables the balls to move freely within the groove. This design promotes smooth and efficient rolling motion.
- Versatility: Deep groove ball bearings can accommodate axial loads in both directions as well, although their primary function is to handle radial loads. This makes them suitable for a wide range of applications where combined radial and axial loads may be encountered.
- Low Friction: The deep groove design, along with the separation of the balls within the groove, reduces friction and allows the bearing to operate with minimal heat generation. This contributes to their efficiency and suitability for various operating conditions.
- Applications: Deep groove ball bearings find applications in diverse industries, including electric motors, conveyors, medical equipment, vacuum technology, and other rotational machinery where radial loads are prevalent.
- Low Maintenance: These bearings are known for their durability and low maintenance requirements. They are often shielded or sealed to protect against contaminants and ensure a longer service life.
Deep groove ball bearings are available in various sizes and configurations to meet the specific needs of different applications. Their simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness make them a popular choice in a wide range of industrial and mechanical systems.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing

Angular Contact Ball Bearings and Deep Groove Ball Bearings serve as pillars in machinery, each excelling in specific domains. Unveiling their differences sheds light on optimizing performance and longevity.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing
Precision takes center stage with Angular Contact Ball Bearings. Their design facilitates axial loads and high-speed applications, making them indispensable in scenarios demanding accuracy and efficiency.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing
Embodying versatility, Deep Groove Ball Bearings thrive in radial loads and a myriad of applications. Their design ensures smooth operation and durability, catering to diverse machinery requirements.
Let’s compare angular contact ball bearing and deep groove
Ball Bearing Comparison Chart
Differences Between Deep Groove Ball Bearings and Angular Contact Ball Bearings:
Contact Angle:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Lower contact angle (~8°)
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Higher contact angle, typically larger than 15°
Axial Load Capacity:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Can accept axial load in both directions
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Primarily designed to support axial loads in one direction
Operating Speed:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Suitable for applications with lower operational speeds
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Designed to support high operating speeds
Space Requirements:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Used when machine space isn’t available for matched bearing sets
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Ideal for applications where high operational speed is required, and space is available for matched bearing sets
Maintenance and Operation Costs:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Low maintenance and operation costs
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: May have higher maintenance and operation costs due to precision requirements and higher operating speeds
Applications:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Commonly used in the medical industry, vacuum technology, applications with dry lubrication and low outgassing, electric motors, and conveyors.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Widely applied in woodworking spindles, machine tool spindles, vacuum pumps, the semiconductor industry, and centrifuges.
Ball Bearing Comparison Chart:
| Ball Bearing Type | Deep Groove | Angular Contact |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | – Can accept axial load in both directions | – Supports high operating speeds |
| – Lower contact angle (~8°) | – Low maintenance & operation costs | |
| Use When | – Machine space isn’t available for matched bearing sets | – High operational speed is required |
| – High operational speed is not required | – Guidance for rotational parts is required | |
| – Guidance for rotational parts is required | – High rigidity & precision is required | |
| Applications | – Medical industry | – Woodworking spindles |
| – Vacuum technology | – Machine tool spindles | |
| – Dry lubrication low outgassing | – Vacuum pumps | |
| – Electric Motors | – Semiconductor industry | |
| – Conveyers | – Centrifuges |
Allow us to quote your precision bearing needs or let our technical support experts “geek out” over your bearing questions.
Radial Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove
“Radial ball bearing” and “deep groove ball bearing” are terms that are sometimes used interchangeably, but it’s important to note the subtle distinctions between the two different ball bearings.
Radial Ball Bearing:
A radial ball bearing is a broad category that encompasses various types of bearings designed to support radial loads, which are forces acting perpendicular to the shaft. Radial ball bearings include different configurations, such as deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, cylindrical roller bearings, and tapered roller bearings, among others. The key characteristic is their ability to support loads primarily in the radial direction.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing:
A deep groove ball bearing is a specific type of radial ball bearing with a distinctive design. It features a deep, uninterrupted raceway that enables the bearing to carry both radial and axial loads in a single direction. The deep groove design facilitates smooth and efficient rolling of the bearing elements (balls) within the groove.
Differences:
- Design: While a deep groove ball bearing is a type of radial ball bearing, not all radial ball bearings are deep groove bearings. Other radial ball bearings, like angular contact or cylindrical roller bearings, have different designs tailored for specific applications.
- Application: Deep groove ball bearings are particularly well-suited for applications where radial and axial loads need to be accommodated simultaneously, and they are commonly used in a wide range of industries. On the other hand, the term “radial ball bearing” is a broader term that can refer to various bearings depending on their specific design and intended use.
In summary, all deep groove ball bearings are radial ball bearings, but not all radial ball bearings are deep groove bearings. The distinction lies in the specific design features of deep groove ball bearings, making them a subset within the broader category of radial ball bearings.
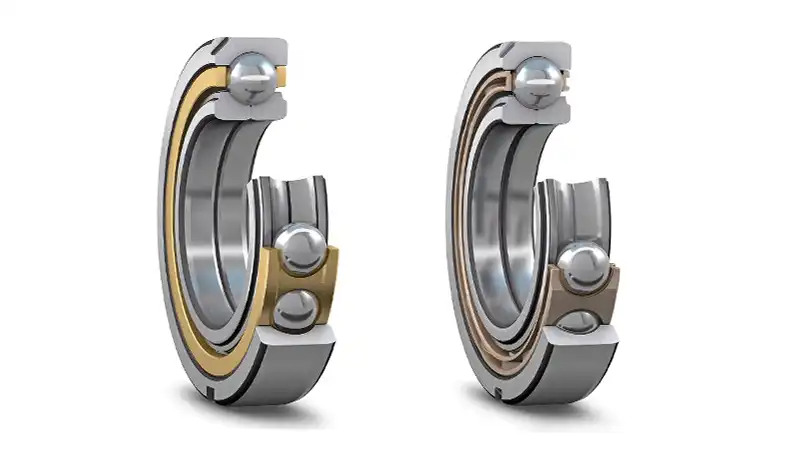
Different in Structure
Deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings share similar inner ring sizes and structures when they have the same inner and outer diameter and width dimensions. However, they exhibit distinct differences in the outer ring size and structure:
Outer Ring Shoulders:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Have double shoulders on both sides of the outer ring groove.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Generally feature a single shoulder on the outer ring.
Outer Ring Curvature:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Possess a specific curvature on the outer ring.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: Exhibit a curvature often greater than that of deep groove ball bearings.
Outer Ring Position:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings: Positioned differently compared to angular contact ball bearings.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings: The position of the outer ring is considered during design and is related to the degree of contact angle.
In summary, while both types share similarities in inner ring size and structure, the distinctions lie in the outer ring design, shoulders, curvature, and positioning.
Now, let’s create a table summarizing the key differences:
| Feature | Deep Groove Ball Bearings | Angular Contact Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Ring Shoulders | Double shoulders on both sides | Generally a single shoulder |
| Outer Ring Curvature | Specific curvature | Curvature often greater |
| Outer Ring Position | Different positioning | Considered in design, related to contact angle |
Different Use of Terms
Deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings are two distinct types of bearings designed for different applications and load conditions. Here are the key differences between them:
Application and Load Capacity:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBB):
- Suitable for bearing radial forces, smaller axial forces, combined radial loads, and moment loads.
- Ideal for applications where the primary load is radial, such as in most common rotating machinery.
- Can handle limited axial loads and moment loads.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings (ACBB):
- Specifically designed to bear single radial loads and larger axial loads, including bidirectional axial loads and moment loads.
- Suited for applications where axial loads are predominant, such as in thrust applications or paired installations with different contact angles.
Limiting Speed:
- Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBB):
- Generally have a lower limiting speed compared to angular contact ball bearings.
- Angular Contact Ball Bearings (ACBB):
- Have a higher limiting speed, making them suitable for high-speed applications where rapid rotation is essential.
Deep groove ball bearings are versatile and suitable for a variety of applications with mixed radial and axial loads, while angular contact ball bearings are specialized for situations where axial loads are significant.
Here is the requested table for a concise overview:
| Feature | Deep Groove Ball Bearings (DGBB) | Angular Contact Ball Bearings (ACBB) |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Radial forces, smaller axial forces, combined radial loads, and moment loads | Single radial loads, larger axial loads, bidirectional axial loads, and moment loads |
| Load Capacity | Primarily radial loads, limited axial and moment loads | Predominantly axial loads, bidirectional axial loads, and moment loads |
| Limiting Speed | Generally lower limiting speed | Higher limiting speed |
This table provides a concise comparison between deep groove ball bearings and angular contact ball bearings based on their key features.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing: Applications Explored

Understanding where each bearing excels is vital for optimal utilization in various applications.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing Applications
- Aerospace Engineering: Navigating the skies demands precision, a realm where Angular Contact Ball Bearings shine.
- Automotive Excellence: From wheel hubs to transmissions, their ability to handle axial loads enhances automotive performance.
- Robotics Realm: Precision in robotics is non-negotiable, and Angular Contact Ball Bearings ensure seamless movement.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Applications
- Conveyor Systems: Handling radial loads effortlessly, Deep Groove Ball Bearings are the backbone of efficient conveyor systems.
- Household Appliances: From washing machines to blenders, their versatility ensures smooth operation in everyday appliances.
- Electric Motor Dynamics: Deep Groove Ball Bearings keep motors humming efficiently with their radial load-handling prowess.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing: Unveiling the Mechanics

Angular Contact Ball Bearing Mechanics
Angular Contact Ball Bearings feature contact angles, ensuring optimal load distribution and reduced friction. This design facilitates precise motion, making them ideal for high-speed applications.
Deep Groove Ball Bearing Mechanics
The deep groove characteristic enhances the radial load-carrying capacity of these bearings. The smooth, uninterrupted raceway design ensures durability and stability in various applications.
Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing: FAQs
Are Angular Contact Ball Bearings suitable for radial loads?
Yes, but their forte lies in axial loads. For predominant radial loads, Deep Groove Ball Bearings are a better fit.
Can Deep Groove Ball Bearings handle high-speed applications?
While they can, Angular Contact Ball Bearings are better suited for high-speed scenarios due to their design focused on precision and reduced friction.
Which bearing type is more versatile?
Deep Groove Ball Bearings take the crown for versatility, seamlessly adapting to a myriad of applications.
Are Angular Contact Ball Bearings noisy?
Not necessarily. Proper lubrication and maintenance ensure smooth and silent operation.
Do these bearings require special installation considerations?
Both types demand precision installation, adhering to manufacturer guidelines for optimal performance.
Can these bearings withstand harsh environmental conditions?
Yes, with proper sealing, both Angular Contact Ball Bearings and Deep Groove Ball Bearings exhibit resilience in challenging environments.
Conclusion:
In the realm of machinery, Angular Contact Ball Bearing vs Deep Groove Ball Bearing presents a choice between precision and versatility. Armed with this knowledge, engineers can elevate their designs, ensuring optimal performance. Embrace the nuances, master the mechanics, and let your machinery thrive.


