Cylindrical roller bearings are the unsung heroes of mechanical systems, silently facilitating smooth motion and reducing friction in various applications.
In this article, we’ll delve into the intricacies of cylindrical roller bearing assemblies, exploring their types, components, assembly process, applications, advantages, and much more.
Types of Cylindrical Roller Bearings
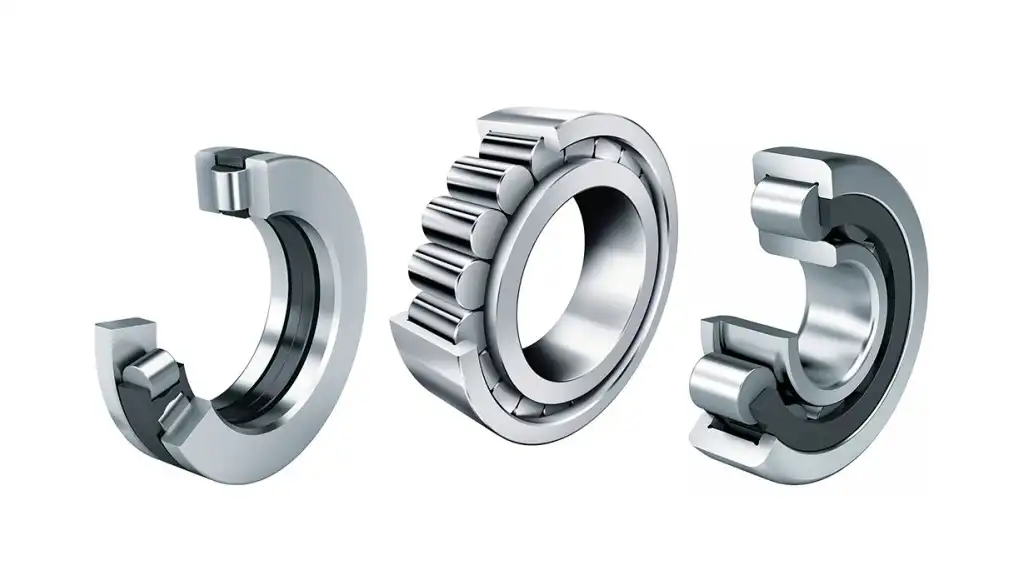

Cylindrical roller bearings come in various types, each designed to meet specific performance and application requirements. Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most suitable bearing for a given purpose. Here are the main types of cylindrical roller bearings:
Single Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
These single row cylindrical roller bearings feature a single set of cylindrical rollers arranged in a line. They are capable of handling radial loads, making them suitable for applications with primarily radial forces.
Double Row Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
As the name suggests, these double row cylindrical roller bearings consist of two sets of cylindrical rollers, allowing them to handle both radial and axial loads. This design provides increased load-carrying capacity.
Full Complement Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
In full complement cylindrical roller bearings, the entire space between the inner and outer rings is filled with cylindrical rollers, without the use of a cage. This design maximizes the number of rollers, enhancing load capacity.
High-Capacity Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
Engineered for applications requiring higher radial load-carrying capacity, these bearings have larger diameter rollers and optimized internal designs to handle heavy loads.
Single Row High-Speed Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
Designed for applications with high-speed requirements, these bearings feature optimized internal geometries and materials to minimize friction and heat generation at elevated speeds.
Thrust Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
Specifically designed to handle axial loads, thrust cylindrical roller bearings have cylindrical rollers arranged parallel to the axis. They are suitable for applications where axial forces are predominant.
Precision Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
These bearings are manufactured to extremely tight tolerances, ensuring high precision in operation. They find application in precision machinery and equipment where accuracy is paramount.
Inch Series Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
These bearings follow imperial unit measurements rather than metric. They are commonly used in industries that still adhere to inch-based specifications.
Split Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
Designed for easy installation and maintenance, split cylindrical roller bearings consist of two halves that can be separated, simplifying the replacement process without disassembling surrounding components.
Custom and Specialty Cylindrical Roller Bearings:
Manufacturers offer customization options to meet unique application requirements. Specialty bearings may include variations in materials, coatings, or designs tailored to specific needs.
Understanding the characteristics and advantages of each type is essential for selecting the right cylindrical roller bearing for a particular application. Factors such as load type, speed, and environmental conditions should be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Components of a Cylindrical Roller Bearing Assembly
Understanding the anatomy of a cylindrical roller bearing is crucial. The assembly consists of an outer ring, inner ring, rollers, and a cage, all working in harmony to provide efficient rotational motion.
Process of Cylindrical Roller Bearing Assembly
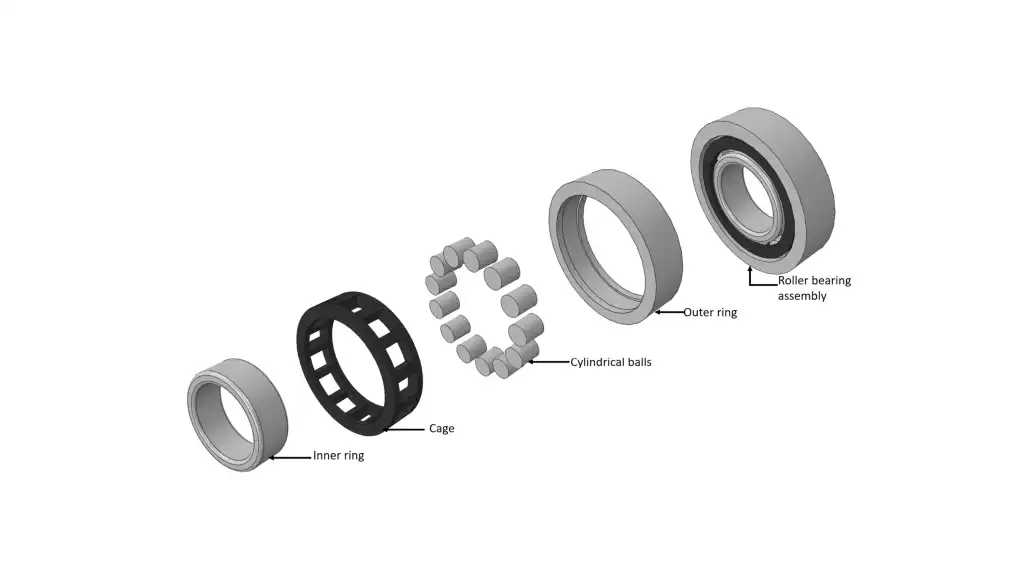
The assembly process of cylindrical roller bearings is a meticulous and precise procedure that ensures the seamless integration of various components.
This process is crucial for the bearing to function efficiently and withstand the demands of its intended application. Here’s a detailed overview of the assembly process:
Machining and Preparation:
The process begins with the machining of the individual components: the outer ring, inner ring, rollers, and cage. Precision is paramount during this phase to guarantee the accurate dimensions required for optimal functionality.
Mounting the Inner and Outer Rings:
The inner and outer rings are carefully mounted onto specialized fixtures. This step involves ensuring the proper alignment of the rings to maintain the desired clearances and fits. Precision mounting is critical for the bearing’s overall performance.
Placing the Rollers:
Cylindrical roller bearings derive their name from the cylindrical shape of the rollers. These rollers are then placed into the channels between the inner and outer rings. The arrangement of rollers in a specific pattern contributes to the bearing’s load-carrying capacity.
Securing the Cage:
Many cylindrical roller bearings utilize a cage to separate and guide the rollers, preventing them from coming into direct contact with each other. The cage is carefully installed, and its design ensures even distribution of load and proper spacing of the rollers.
Lubrication:
Lubrication is a critical step to reduce friction and dissipate heat during operation. The bearing is thoroughly lubricated with a suitable grease or oil, ensuring that all moving parts are adequately covered for optimal performance and longevity.
Sealing (if applicable):
In applications where contamination must be minimized, sealing components are added to protect the internal parts of the bearing. This step is crucial for bearings operating in harsh environments or exposed to debris.
Quality Control Checks:
After assembly, each bearing undergoes rigorous quality control checks. These checks may include dimensional inspections, torque testing, and visual inspections to identify any anomalies that could affect the bearing’s performance.
Packaging:
Once the bearings pass quality control, they are carefully packaged to prevent any damage during transportation and storage. Proper packaging also ensures that the bearings remain free from contaminants until they are ready for use.
Documentation and Traceability:
Documentation is crucial for traceability and quality assurance. Each bearing is assigned a unique identifier, and relevant data, such as manufacturing date and specifications, is recorded for future reference.
Storage:
Finished bearings are stored in controlled environments to maintain their integrity until they are ready to be shipped to end-users or manufacturers for incorporation into larger systems.
Understanding and adhering to each step in the assembly process is vital for producing high-quality cylindrical roller bearings that meet the stringent requirements of diverse industries. This meticulous approach ensures that the bearings perform reliably in various applications, from automotive systems to industrial machinery.
Cylindrical Roller Bearing Applications

Cylindrical roller bearings find widespread application across various industries due to their versatility and ability to handle different types of loads. Here are some common applications of cylindrical roller bearings:
Automotive Industry:
Cylindrical roller bearings are extensively used in automotive applications, including wheel hubs, transmissions, and engine components. Their ability to handle radial loads makes them crucial for supporting rotating shafts in vehicles.
Industrial Machinery:
In industrial settings, cylindrical roller bearings play a vital role in various machinery, such as pumps, compressors, and conveyors. They are preferred for their high radial load capacity and compact design.
Aerospace Applications:
Aerospace systems demand precision and reliability, and cylindrical roller bearings are used in aircraft engines, landing gear, and other critical components. Their ability to handle high loads makes them suitable for aerospace environments.
Electric Motors:
Cylindrical roller bearings are integral components in electric motors, where they support the rotating shafts and handle radial loads efficiently. Their versatility and high load-carrying capacity contribute to motor performance.
Mining and Quarrying Equipment:
Heavy-duty machinery used in mining and quarrying relies on cylindrical roller bearings for their ability to withstand substantial radial loads. They are commonly found in crushers, screens, and conveyor systems.
Railway Systems:
Cylindrical roller bearings are employed in railway applications, including wheelsets and axleboxes. Their robust design allows them to endure the dynamic loads experienced in rail transport.
Construction Equipment:
Construction machinery, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, utilize cylindrical roller bearings for their durability and load-bearing capabilities. They contribute to the reliable performance of these heavy-duty machines.
Wind Turbines:
In the renewable energy sector, cylindrical roller bearings are used in wind turbine generators. They support the main shaft and withstand the varying loads imposed by wind conditions.
Paper and Pulp Industry:
Cylindrical roller bearings are employed in paper and pulp processing machinery, where they provide reliable support for rotating components like rollers and shafts.
Textile Machinery:
Textile manufacturing equipment relies on cylindrical roller bearings for smooth operation in various components, including spinning machines and looms.
Medical Equipment:
Precision is crucial in medical devices, and cylindrical roller bearings find application in various medical equipment, ensuring smooth and reliable movement in components like scanners and imaging devices.
Power Generation:
Cylindrical roller bearings are utilized in power generation equipment such as turbines and generators. Their robust design and high load capacity contribute to the efficiency and reliability of power generation systems.
Oil and Gas Industry:
Critical equipment in the oil and gas sector, including pumps and drilling machinery, benefit from the use of cylindrical roller bearings to handle demanding operational conditions.
Machine Tools:
Precision machine tools, such as lathes and milling machines, incorporate cylindrical roller bearings for their ability to provide accurate and stable rotational motion.
Robotics:
Cylindrical roller bearings are essential in robotics, supporting the joints and movement mechanisms of robotic arms and systems.
These diverse applications highlight the adaptability of cylindrical roller bearings across industries, showcasing their importance in ensuring the smooth and reliable operation of various mechanical systems.
Advantages of Cylindrical Roller Bearings

Cylindrical roller bearings offer several advantages that contribute to their widespread use in various industries.
Here are some key advantages:
High Radial Load Capacity:
Cylindrical roller bearings are designed to handle high radial loads, making them suitable for applications where the primary force is directed perpendicular to the shaft.
Compact Design:
Their cylindrical shape and efficient design allow for a compact form factor, making cylindrical roller bearings ideal for applications with limited space.
Versatility in Applications:
Cylindrical roller bearings are versatile and can accommodate different types of loads, including radial and axial loads. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
High-Speed Performance:
Some types of cylindrical roller bearings are designed to operate at high speeds, making them suitable for applications where rotational speed is a critical factor.
Ease of Installation:
Cylindrical roller bearings are relatively easy to install and replace, especially in applications where accessibility might be a challenge. This ease of installation contributes to reduced downtime during maintenance.
Reduced Friction:
The design of cylindrical roller bearings minimizes friction between the rollers and the raceways, leading to more efficient operation and reduced energy consumption.
High Temperature Resistance:
Certain types of cylindrical roller bearings are engineered to withstand elevated temperatures, making them suitable for applications in high-temperature environments.
Cost-Effectiveness:
Cylindrical roller bearings offer a cost-effective solution for various applications, providing reliable performance at a reasonable cost.
Ease of Maintenance:
Regular maintenance, including inspection and lubrication, is relatively straightforward with cylindrical roller bearings. This contributes to their longevity and overall reliability.
Accommodation of Misalignment:
Cylindrical roller bearings can accommodate slight misalignments between shaft and housing, providing flexibility in installation and reducing the likelihood of premature wear.
Quiet Operation:
The design of cylindrical roller bearings, especially those with optimized internal geometries and precision manufacturing, contributes to quiet and smooth operation.
Long Service Life:
With proper maintenance and appropriate operating conditions, cylindrical roller bearings can offer a long service life, contributing to cost savings over time.
Standardization:
The standardized dimensions and specifications of cylindrical roller bearings make them interchangeable across different manufacturers, providing convenience in sourcing and replacement.
High Rigidity:
Cylindrical roller bearings exhibit high rigidity, ensuring stability in applications where precision and stiffness are critical factors.
Sealing Options:
Many cylindrical roller bearings come with sealing options to protect against contaminants, extending the bearing’s life in challenging operating environments.
These advantages collectively make cylindrical roller bearings a preferred choice in numerous applications, where reliability, efficiency, and ease of maintenance are crucial considerations.
Maintenance Tips for Cylindrical Roller Bearings
Regular inspection and proper lubrication are paramount for ensuring the longevity of cylindrical roller bearings. Monitoring temperature fluctuations provides early indications of potential problems.
Choosing the Right Cylindrical Roller Bearing

Choosing the right cylindrical roller bearing is a critical decision that directly influences the performance, longevity, and efficiency of a mechanical system. Here are the key considerations to help guide the selection process:
Load Requirements:
Determine the type and magnitude of loads the bearing will experience. Cylindrical roller bearings are well-suited for radial loads, while certain designs can handle both radial and axial loads. Understanding the load conditions ensures the bearing’s capacity aligns with the application’s demands.
Speed Ratings:
Consider the rotational speed requirements of the application. Different cylindrical roller bearings are designed to operate at varying speeds. High-speed applications may require bearings with optimized internal geometries and materials to reduce friction and heat generation.
Operating Conditions:
Evaluate the environmental factors, such as temperature, moisture, and potential contaminants, that the bearing will be exposed to. Choose bearings with appropriate seals or shields to protect against adverse conditions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Precision Requirements:
Precision cylindrical roller bearings are available for applications demanding high levels of accuracy. Consider the tolerances and precision classes required for the specific machinery or equipment to achieve desired performance levels.
Mounting and Disassembly Ease:
Ease of installation and maintenance is crucial. Consider whether the application allows for straightforward mounting and disassembly. Split cylindrical roller bearings can be advantageous in situations where accessibility is challenging.
Lubrication:
Select the appropriate lubrication method based on the application’s requirements. Some bearings are pre-greased, while others may require periodic lubrication. Proper lubrication is essential for reducing friction, dissipating heat, and preventing premature wear.
Size and Dimensions:
Ensure the selected bearing’s dimensions match the shaft and housing requirements. Precise sizing prevents misalignment issues and contributes to the overall stability and efficiency of the system.
Cage Design:
Consider the type of cage used in the bearing. Cages help retain and guide the rollers, affecting the distribution of load and overall performance. Different cage materials and designs may suit specific applications better.
Misalignment Tolerance:
Assess the potential for misalignment in the application. Some cylindrical roller bearings can accommodate misalignment better than others. Choosing a bearing with appropriate misalignment tolerance contributes to smoother operation.
Environmental Impact:
Consider the environmental impact of the bearing, especially if sustainability is a priority. Some manufacturers offer eco-friendly options with recyclable materials and reduced environmental footprint.
Consultation with Experts:
Seek guidance from bearing experts or manufacturers. Their expertise can provide valuable insights into selecting the most suitable cylindrical roller bearing for the specific application, taking into account unique requirements and challenges.
Budgetary Considerations:
While ensuring the bearing meets all technical requirements, consider the budget constraints. Various options are available at different price points, and finding the right balance between performance and cost is crucial.
Application-Specific Features:
Explore if there are application-specific features offered by certain cylindrical roller bearings that could enhance performance. This may include features like high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, or enhanced sealing.
Brand Reputation:
Consider the reputation of the bearing manufacturer. Established and reputable brands often provide higher-quality bearings with consistent performance and reliability.
Review Past Performance:
If applicable, review the performance of similar bearings in past applications. Understanding the track record of specific bearings in similar conditions can provide valuable insights into their suitability.
Taking a comprehensive approach to these considerations ensures that the chosen cylindrical roller bearing is well-matched to the specific requirements of the application, contributing to optimal performance and extended service life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cylindrical roller bearing assembly plays a pivotal role in the seamless operation of various mechanical systems. Its versatility, coupled with ongoing innovations, positions it as a cornerstone in engineering solutions, ensuring efficiency and reliability.

