Ball bearings, often overlooked yet ubiquitous, play a pivotal role in various industries, providing seamless motion and reducing friction. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of ball bearings, exploring their history, types, applications, and the latest advancements in technology.
What Are Ball Bearings
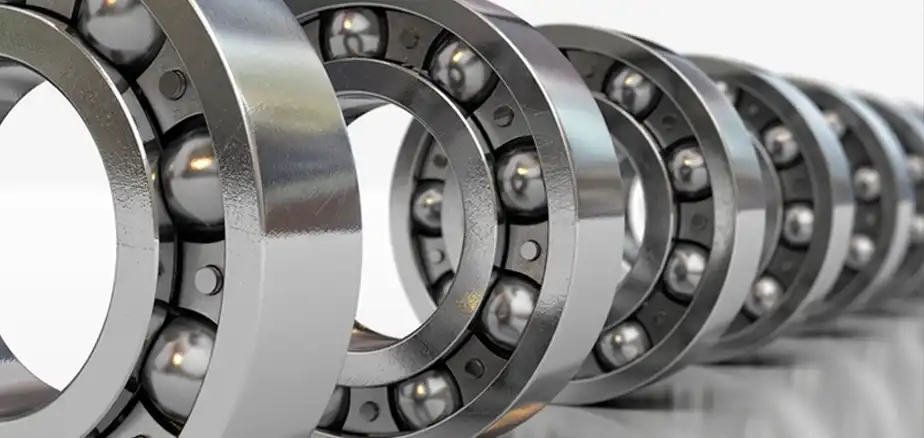

Ball bearings are mechanical components designed to facilitate smooth motion by reducing friction between moving parts. They consist of small metal balls held within a ring, enabling rotational movement with minimal resistance.
From automotive to manufacturing, ball bearings are integral in numerous applications. Their ability to enhance efficiency and durability makes them indispensable in modern machinery.
History of Ball Bearings

Early Developments
The concept of ball bearings dates back to ancient times, with early prototypes found in artifacts from the Roman era. However, it wasn’t until the 19th century that advancements led to the widespread use of ball bearings.
Evolution over the Years
Over the years, ball bearing designs have evolved, incorporating new materials and manufacturing techniques. This evolution has resulted in increased load capacity, reduced friction, and improved overall performance.
Types of Ball Bearings
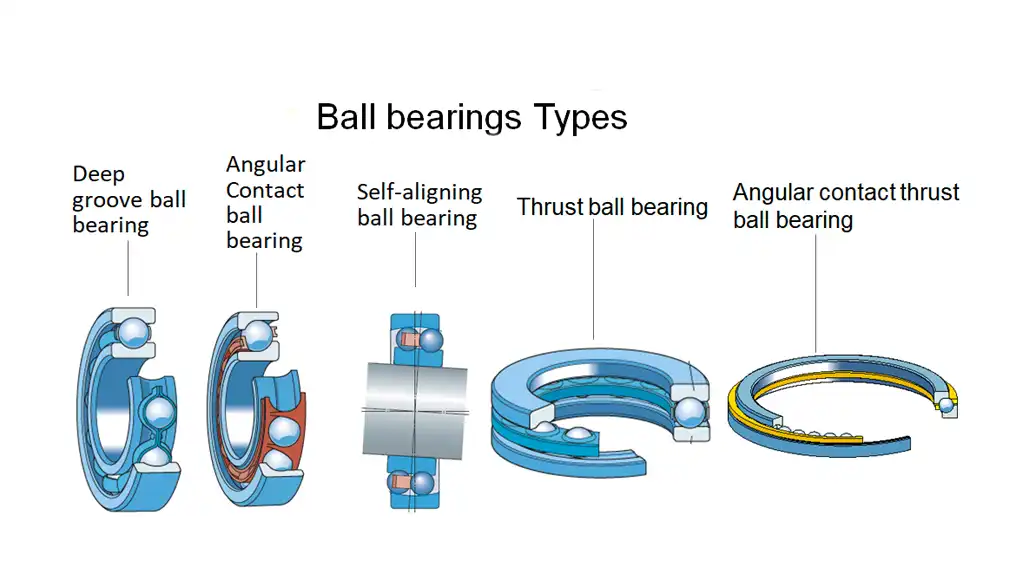
Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are the most common type, suitable for radial and axial loads. Their design allows them to handle high-speed applications with ease.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are designed to handle combined radial and axial loads. They find applications in machinery where precision and high-speed performance are crucial.
Self-again Ball Bearings
Self-aligning ball bearings are designed to accommodate misalignment between the shaft and housing, providing flexibility in various applications.
Thrust Ball Bearings
Thrust ball bearings are specialized for axial loads, ensuring smooth motion in applications such as automotive transmissions.
Angular Contact Thrust Ball Bearings
Angular contact thrust ball bearings are designed to handle axial loads in combination with high radial loads. This type is suitable for applications where both precision and thrust capacity are critical.
How Ball Bearings Work

Basic Mechanism
The fundamental working principle involves the rotation of metal balls between two rings, minimizing friction and distributing the load evenly.
Role in Reducing Friction
The reduction of friction is paramount in machinery, and ball bearings excel in this regard, contributing to increased efficiency and prolonged lifespan.
Ball Bearing Applications in the Automotive Industry
Engine Components
Ball bearings are extensively used in engines, providing support to rotating components and ensuring smooth operation.
Wheel Bearings
In automotive wheel assemblies, ball bearings contribute to reduced friction, enhancing fuel efficiency and overall performance.
Machinery and Equipment
In manufacturing and industrial settings, ball bearings support the smooth operation of machinery, from conveyor belts to precision equipment.
Role in Manufacturing Processes
Precision manufacturing relies on ball bearings to maintain accuracy and reduce wear in machinery components.
Advantages of Using Ball Bearings
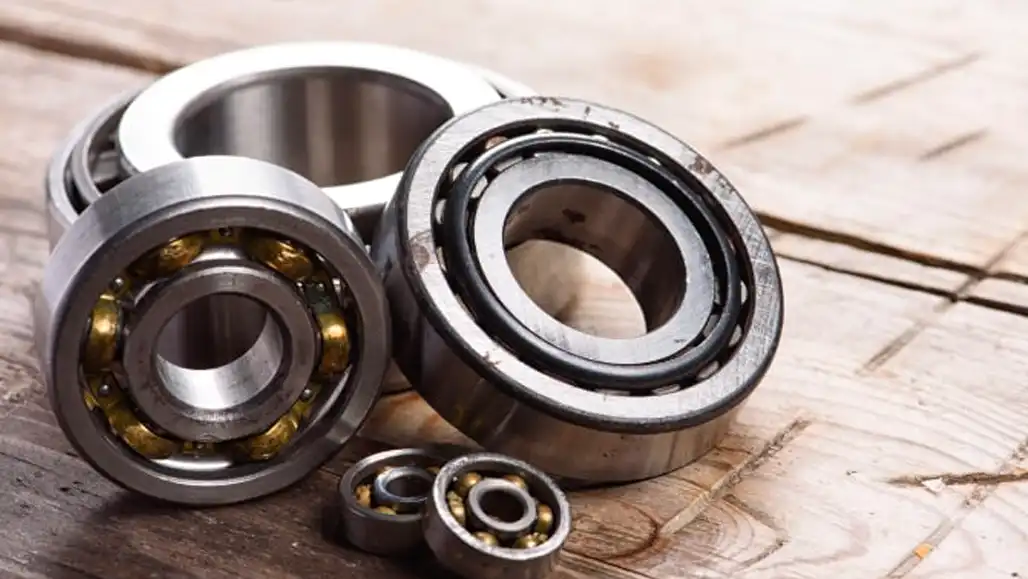

Efficiency and Durability
Ball bearings contribute to energy efficiency and equipment durability, making them a cost-effective choice for various applications.
Cost-Effectiveness
The long lifespan and minimal maintenance requirements of ball bearings translate to cost savings over time.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Maintenance Issues
Regular maintenance is crucial for ball bearings. Lack of lubrication and contamination can lead to premature failure, emphasizing the need for proactive maintenance.
Lubrication Challenges
Proper lubrication is essential for optimal performance. Choosing the right lubricant and adhering to maintenance schedules mitigate potential challenges.
Innovations in Ball Bearing Technology
Recent Advancements
Recent technological advancements include the use of advanced materials, precision manufacturing techniques, and innovative designs, pushing the boundaries of ball bearing capabilities.
Future Trends
The future promises even more sophisticated ball bearing technologies, with a focus on sustainability, increased load capacity, and enhanced reliability.
Selecting the Right Ball Bearings
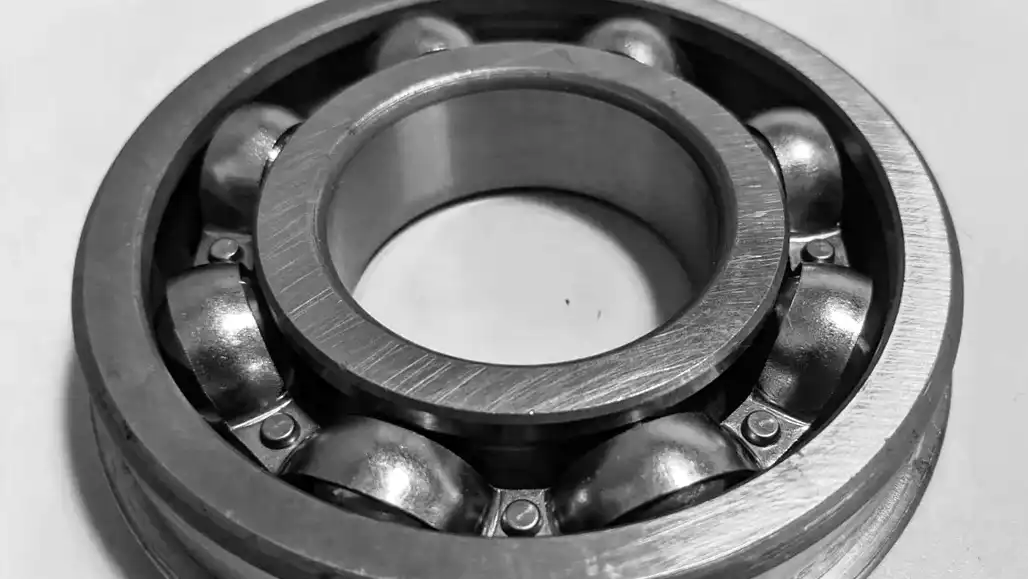

Choosing the appropriate ball bearings for a specific application is a critical decision that directly impacts the performance, reliability, and longevity of machinery.
Here’s a comprehensive guide on selecting the right ball bearings, considering various factors to ensure optimal functionality.
Load Capacity
The load capacity is a crucial factor in determining the right ball bearings for an application. Different types of ball bearings are designed to handle specific load types—radial, axial, or a combination of both. Understanding the load requirements of the machinery is essential to choosing bearings that can effectively support and distribute the applied loads.
Speed Requirements
The speed at which machinery operates is a key consideration. Certain ball bearings, such as angular contact ball bearings, are specifically designed for high-speed applications. It’s essential to match the bearing’s speed capabilities with the operational requirements of the machinery to ensure optimal performance and prevent issues like overheating.
Environmental Conditions
The environment in which machinery operates plays a significant role in selecting the right ball bearings. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to contaminants can impact bearing performance. Specialized bearings with features like sealed or shielded designs may be necessary to protect against environmental factors.
Precision and Tolerance
Precision requirements vary across applications, especially in industries like aerospace and manufacturing. Choosing bearings with the appropriate tolerance and precision ensures that machinery operates with the required accuracy. Precision ball bearings are essential for applications where tight tolerances and minimal deviations are critical.
Tips for Ball Bearing Maintenance
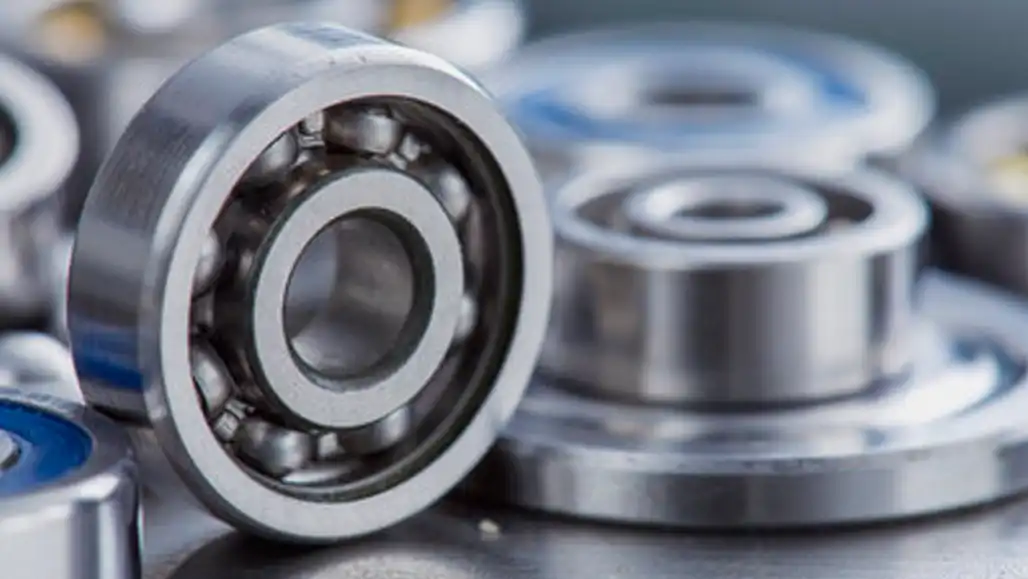

Lubrication Requirements
Proper lubrication is fundamental for the longevity and performance of ball bearings. Understanding the specific lubrication requirements of the chosen bearings is essential. Factors such as speed, temperature, and load influence the choice of lubricant and the frequency of lubrication intervals. Adhering to manufacturer recommendations for lubrication ensures optimal functioning and prevents premature wear.
Regular Inspections
Routine inspections are vital to identify potential issues before they escalate. Regularly checking for signs of wear, contamination, or misalignment helps detect problems early on. This proactive approach allows for timely maintenance and replacement, preventing costly downtime and avoiding damage to other machinery components.
Monitoring Operating Conditions
Continuous monitoring of operating conditions provides valuable insights into the performance of ball bearings. Utilizing sensors and monitoring systems can help track factors such as temperature, vibration, and load variations. Early detection of abnormal conditions enables timely intervention, reducing the risk of unexpected failures.
Environmental Impact
Considering the environmental impact of ball bearings aligns with sustainability goals. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on eco-friendly materials and production processes. Choosing bearings from suppliers committed to sustainable practices contributes to minimizing the environmental footprint of machinery.
Recycling and Disposal
Efforts are underway to develop recycling methods for ball bearings. As part of responsible manufacturing practices, selecting bearings that are recyclable or come from suppliers engaged in recycling initiatives supports the industry’s move towards a circular economy. Proper disposal methods also play a role in reducing environmental impact.
In conclusion, selecting the right ball bearings involves a thorough understanding of the specific requirements of the machinery and the operating environment. Whether it’s load capacity, speed, precision, or environmental considerations, each factor contributes to the overall performance and longevity of ball bearings. Regular maintenance, adherence to lubrication practices, and a focus on sustainability further enhance the reliability and efficiency of the chosen bearings, ensuring optimal functionality throughout their lifespan.
Conclusion
Recap of Key Points
In conclusion, ball bearings are indispensable in modern machinery, contributing to efficiency, durability, and overall performance.
Significance in Modern Industries
Their significance in diverse industries underscores the need for continued innovation and responsible usage to meet the evolving demands of technology.
